Suggestions for the bundled combustion test of flame-retardant cloth wire products
In the flame retardant test standard for bundled wires and cables GB/T 18380.33~36, in addition to the flame retardant category D, it is clearly stated that it is applicable to “small cables with an outer diameter not exceeding 12 mm and a cross-section not exceeding 35 mm2” (refer to GB/T here) The original text of the IEC 60332-3-25:2018 standard corresponding to 18380.36 has been partially adjusted. The original English text of IEC 60332-3-25 is “This document relates only to small cables of overall diameter 12 mm or smaller and cross-section of 35 mm2 or smaller installed on the test ladder to achieve a nominal total volume of non-metallic material of 0.5 L/m of test sample.”), the others do not give clear restrictions on wire and cable products in the scope of application. At the same time, the widely adopted general standard GB/T 19666 does not provide detailed definitions for the application of different flame retardant categories in cloth wire products. Therefore, there are a large number of ZA~ZD fully flame retardant category flame retardant wire products on the market. , such as Z(A,B,C,D)-BV 450/750V, WDZ(A,B,C,D)-BYJ 450/750V, etc.

However, attention should be paid to the restrictions imposed by the sample installation conditions on wire and wire products in the GB/T 18380.33~35 (Flame Retardant Class A, B, C) standards.
1
Space arrangement requirements
There are clear requirements in the installation of specimens of flame-retardant classes A, B and C: “For cables with at least one conductor cross-section exceeding 35 mm2, each cable specimen section should be fixed on each side of the steel ladder using metal wires. The cable sample section should be installed in a single layer in front of the steel ladder. The interval between cable sample sections should be 0.5 times the cable diameter, but not more than 20 mm. Regardless of whether a standard steel ladder or a wide steel ladder is used, the edge of the sample The minimum distance from the vertical surface on the inside of the steel ladder shall be 50 mm. The maximum width of the specimen on the standard steel ladder shall be 300 mm, and the maximum width of the specimen on the wide steel ladder (category A only) shall be 600 mm.”
2
Number of sample installations
According to the conventional structure of cloth wire products and the volume requirements of non-metallic materials for different flame retardant category tests, the number of samples of cloth wires with conductor nominal cross-section greater than 35 mm2 in flame retardant Class A, Class B and Class C tests can be roughly calculated as follows: As shown in Table 2. From the comparison, it can be seen that for wires with conductor nominal cross-section greater than 35 mm2, according to the spacing arrangement and installation number requirements of the above analysis, there are no corresponding specifications of wires of flame-retardant Class A and Class B that can meet the test sample installation requirements. Category C can only meet some large specifications.
Table 2 Installation of flame retardant test samples for wire and cable products with a conductor nominal cross-section of 35 mm2 or more
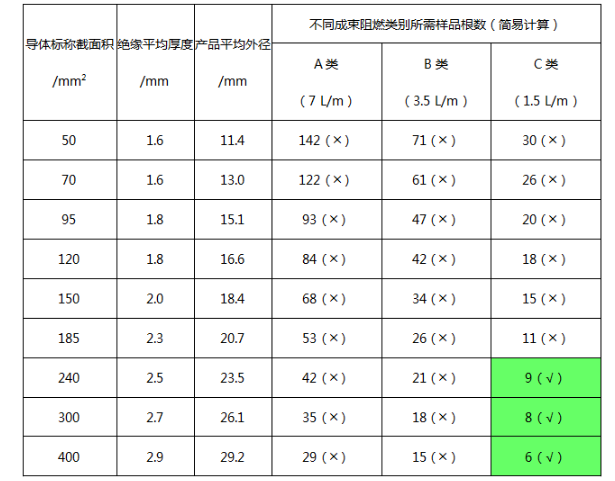
Note:
1. Due to the limitation of the width of the steel ladder, the symbol (╳) indicates that the specimen cannot be installed for testing, and (symbol √) indicates that the specimen can be installed for testing.
2. The wiring involved in this article generally refers to: single-core unsheathed wires with rated voltage 450/750V and below, and a maximum specification of a conductor with a nominal cross-section of 400 mm2.
3. The value of the average insulation thickness refers to the specified value of insulation thickness in GB/T 5023.3 (an additional 0.2~0.3mm); the average outer diameter calculation formula: average outer diameter = conductor outer diameter + 2X average insulation thickness, where the conductor outer diameter Refer to the nominal calculated value of conductor outer diameter for stranded conductors (type 2) in IEC60719.
In addition, GB/T 18380.36 clearly states that flame retardant Class D is suitable for “small cables with an outer diameter not exceeding 12 mm and a cross-section not exceeding 35 mm2”. Coincidentally, as a typical single-core unsheathed cable product, GB/ For the BV and RV types in the T 5023.3 standard, and the BYJ and RYJ types in the JB/T 10491 standard, the upper limits of the average outer diameter of the 35 mm2 specification wire are 10.9 mm and 11.7 mm respectively. This data is consistent with the conditions for flame retardant Class D restrictions. (Conductor nominal cross-section 35 mm2 and below and outer diameter 12 mm and below) are consistent, which also reflects that for wiring products with conductor nominal cross-section 35 mm2 and below, the most direct match is flame-retardant Class D. Relevant evidence for this can also be found in other product standards. For example, the low-smoke halogen-free flame-retardant cable structures specified in GB/T 12528-2008 “Cables for Rail Transit Vehicles with AC Rated Voltage 3kV and Below” are both typical single-core Unsheathed wire structure, in the standard 7.4.8 bundled cable combustion test clause, the bundled combustion test of standard low-smoke halogen-free cables is limited to flame-retardant Class C and D cables with an outer diameter greater than 12 mm It is required to pass Category C, and those not larger than 12 mm are required to pass Category D.
Summary:
Analysis based on relevant standards can be seen:
1) Wires with a nominal cross-section exceeding 35mm2 neither meet the sample installation requirements for bundled flame-retardant Class A and Class B tests nor the applicable scope of flame-retardant Class D tests. Only some specifications are applicable to flame-retardant testing. Category C test.
2) Wires with a nominal cross-section of 35mm2 and below can be applied to bundled flame-retardant categories A, B, C, and D because there are no restrictions in the standard. However, judging from the scope description of GB/T 18380.36, the most directly matching It is flame retardant class D.
Suggestions for bundled combustion test of flame-retardant cloth wire products
For flame-retardant cloth wire products, how to choose the bundled combustion test method is one of the focuses of the industry.
First of all, for flame-retardant cloth wire products with conductor nominal cross-section exceeding 35 mm2, since they neither meet the applicable scope of flame-retardant class D nor meet the test sample installation of flame-retardant classes A and B.Therefore, only the flame retardant Class C test specified in GB/T 18380.35 should be selected for the flame retardant test of wiring within this range.
For flame-retardant wire and cable products with a conductor nominal cross-section of 35 mm2 and below, although in principle they can be applied to flame-retardant classes A to D, if samples are selected for testing in each flame-retardant category, there will be a sharp increase in the number of tests. The cost of testing, sample cost and even environmental protection pressure, so in actual quality control activities such as sampling, certification or evaluation, the coverage principle is usually used to select representative samples for a certain flame retardant category test, and the priority flame retardant test category is usually sorted For Category A – Category B – Category C – Category D. However, whether this kind of sorting is the optimal solution for wiring products is questioned, especially for wiring products in the category of small cables where the “nominal cross-section of the conductor does not exceed 35 mm2 and the outer diameter does not exceed 12 mm”.
In order to verify relevant data and draw guidance, the China Quality Certification Center (CQC) and Shanghai Lianhui Testing Technology Co., Ltd. (ISTCW) teamed up with eight mainstream domestic wire and cable manufacturers to organize flame retardant verification tests for bundled wires. In the verification test, two typical home improvement wire specifications of two representative insulation materials were selected as verification samples, involving a total of 5 groups of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) insulated ZA-BV 450/750V 2.5 wires and 5 groups of cross-linked wires. Polyolefin (XLPO) insulated WDZA-BYJ 450/750V 2.5 wire. Cable manufacturers strictly follow the wire structure requirements specified in the verification test plan and uniformly prepare verification samples that meet the standard requirements. Subsequent verification samples strictly follow the requirements of the GB/T 18380.33~36-2008 standard and adopt relatively unified sample installation and test operation requirements. , in the same test equipment, 10 groups of verification samples were intensively carried out bundled flame retardant Class A, Class B, Class C and Class D combustion tests (a total of 40 batches of tests), and the vertical flame spread after the test was measured. distance.
Considering that the judgments of different categories of flame retardant tests are: the carbonization range on the sample should not exceed 2.5 m above the bottom edge of the blowtorch. If according to the inertial understanding of flame retardancy, the flame retardant performance of Class A is better than (covering) Class B, Class C to Class D, that is, the severity of the bundled flame retardant test is considered to be A>B>C>D, then It can be inferred that after the same sample undergoes tests of different flame retardant categories, the carbonization height index reflecting the flame extension should show the pattern A>B>C>D.






