01 Reproducibility problem of yarn dyeing
Under the same process prescription, process dyeing materials, etc., the result is that there is always color difference between different batches . The competitiveness of textile companies, especially yarn dyeing factories, lies in just-in-time production and first-time success, and the two are inseparable. Just-in-time production can quickly respond to the market and produce products in the shortest time. First-time success means that the product should meet quality requirements.
Product quality generally includes two aspects: intrinsic quality and appearance quality, which mainly require reproducibility. The color and light reproducibility of dyed yarn is poor. The essence is that the dyes used in different batches of dyeing have poor reproducibility. To achieve reproducible yarn dyeing, all factors in the dyeing process must be controlled.
Generally, poor reproducibility (i.e. vat difference) means that during intermittent dyeing, the same dyed objects (yarns) are dyed with the same dyeing materials, prescriptions and processes. However, there are color differences (different shades, different shades, or both) between dyed objects in different dyeing batches.
Occasions where poor reproducibility often occurs are generally: between small samples, between small samples and medium samples, between medium samples and large samples, between small samples and large samples; between different dyeing machines, or between two dyeing machines The capacity is different, or the capacity is the same but the manufacturer is different, or even between dyeing machines with the same capacity in the manufacturer; between different dyeing batches of the same dyeing machine.
02 Reasons for poor dyeing reproducibility
There are many reasons for poor color reproducibility. The reasons for color difference in yarn package dyeing include: yarn, dyeing materials, process design and control, operation, equipment, water quality, etc. Generally speaking, they are divided into external objective factors and human subjective factors.
Objective factors
1. Yarn
Some certain factors in the growth process of cotton fiber Differences will produce differences in fiber quality. Therefore, the quality of yarns produced by different manufacturers is different, resulting in different dye absorption properties of the yarns, and the reproducibility after dyeing will be different. In addition, the thickness (linear density) of cotton fibers is different, and the apparent depth after dyeing is also different. For example, after cotton yarns 7S and 40S are dyed, the appearance of 7S will be darker, the thicker ones will be darker, and the thinner ones will be lighter. The twist, cotton mix, and moisture regain of the yarn will also affect the reproducibility of the shade. Even fibers with the same components and specifications will have different dyeing properties due to fluctuations in the production process. As for fibers re-spun from recycled waste, the dyeing properties are also different from conventional fibers. For dyed yarn, when the fiber batch changes, small sample testing should be carried out, and the prescription should be adjusted if necessary before it can be officially put into production. (If it is a blended yarn of two or more fibers, if the blending ratio fluctuates and the dyeing prescription is different, vat differences will also occur in batch dyeing).
2. Dyeing materials
Dye production is mostly organic synthesis reaction, with long process and complex reaction. Fluctuation of any process parameters during production will cause The composition and quality of the product deviate. Dyes with the same structure have different dye quality due to differences in technology, equipment, management, operation, and control levels; the same dyes in different batches of the same company also have reproducibility problems, which will also affect the dyeing performance and the quality of the dyed objects. Differences in color, light and shade. In addition, the sensitivity (dependence) of various process conditions for dyeing with different dye degrees is different. The more sensitive the dye (the greater the dependence), the worse the reproducibility. In addition, the different mixing formulas of dyes provided by dye factories will also have a great impact on the dyeing performance and shade. At the same time, the mixing of dyes also has problems with reproducibility and mixing uniformity.
Another point is that dyes also have their own storage cycles. Some dyes (such as reactive and soluble vat dyes) are easy to deteriorate if stored for improper time or conditions. Most dyes will absorb moisture and deliquesce, thus directly affecting the quality of the dye. Strength points. Sometimes there will be differences in shade and strength between the upper, middle and lower layers of the same dye (shade differences often occur in blended dyes). This may be due to the delamination of dyes and additives with different particles and specific gravity during transportation. Of course, we do not rule out blending quality issues caused by individual middlemen.
3. Instruments and equipment
Dyeing bobbins, beam coils and scales. Different types of bobbins have different sealing conditions, so the effective flow rate is also different. Even if the main pump discharges the same flow rate, the difference can reach 10% to 40%. The degree of dye liquor leakage is different, so that the actual flow rate circulating in the yarn Different amounts of dye liquor lead to different amounts of dye carried on the yarn, resulting in poor reproduction of shades. Different forms and designs of bobbin penetration rates change, which will also cause the flow rate to change, and the cycle frequency and number of cycles will also change, resulting in poor filament dyeing vats. Different dyeing machines have different bottom discs, top discs, and top locks with different seals and leaks, so the effective flow rate is different, and the cylinder difference cannot be controlled. There must also be strict selection of scales for weighing dyes. Scales with different precisions should be used for different weighing ranges. Do not use large scales to weigh small amounts. The general weighing tolerance range is as follows:
Weighing tolerance range table
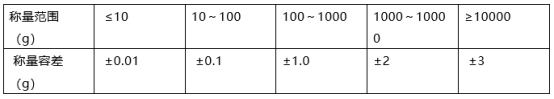
Therefore, Different measuring ranges and related sensors are equipped when weighing dyes.�Because managers have not formulated correct and strict operating methods, operators are left to their own devices. What’s more, process changes often occur on manual or semi-automatic equipment. The non-reproducibility of the process will lead to poor dyeing reproducibility.
6. Management issues
Dyeing reproducibility involves not only the dyeing process, but also the entire production process. It is a systematic project, which also has something to do with management. Closely related, such as gray yarn and semi-finished products management, dye management, measurement management, technical management and laboratory management: the same batch of gray yarn should be used for the same color number. If you want to change, you have to repeat the sample. It should be “practice first, first practice”. “Use”, “Reuse after training”, “Same color and same batch”; dyes manufactured by different manufacturers, even dyes from different batches of the same factory, will have reproducibility problems, etc. Due to the lack of attention in management, the It is easy to cause poor reproducibility between batches in the dyeing of package yarns.
7. Laboratory tracking of large-scale production
First of all, the way the laboratory supports production is not to transfer processes and recipes to large-scale production, but to It is to simulate large-scale production in the laboratory and achieve high reproducibility of large-scale production-laboratory. When there is a hue discrepancy in large-scale production and color correction is required, the laboratory should work together to complete the process. The laboratory should analyze and test the information provided by large-scale production (color and light differences between large and small samples) to find out the differences between the large and small sample production of each dye. Correlation to reduce color correction.
In addition, in order to achieve large-scale production – attaching great importance to the laboratory, we must first achieve reproducibility from laboratory to laboratory, and reproducibility from large-scale production to large-scale production, otherwise large-scale production The reproducibility with the laboratory is poor.
03 Solutions and measures
Poor reproducibility of yarn dyeing is often encountered in yarn production. Based on the dyeing situation of yarn in our factory and my partial understanding of production operations, I feel that management should be strengthened in the following aspects to ensure the reproduction of yarn dyeing from a basic level:
1. Selection of equipment
Equipment should be selected that can ensure the dyeing quality of the product and shorten the dyeing time. It should adopt a self-drop top lock device and use the internal flow of the equipment to naturally compress the package yarn so that it can be placed on the equipment. Provide basic conditions for reproducibility;
2. Winding quality
In order to ensure dyeing penetration, the density of the package yarn is generally controlled between 0.35 and 0.40 time, the density after compression should be controlled between 0.41 and 0.46.
3. Dyeing materials
Select the types of dyes carefully, pay attention to the inspection between dye batches, and ensure the cleanliness of the dye room Ventilate and dry, and protect the dye from moisture.
4. Process parameters
The formulation and control of process parameters are the key to dyeing. A good dyeing process must have a set of Supported by scientific and reasonable parameters. For example, when using salt and alkali, we should pay attention to the method and time of adding materials. We can use the salt prepared in advance to reduce the aggregation and precipitation of dyes caused by insufficient salt dissolution, resulting in poor dyeing reproducibility;
5. Proofing and setting out
The laboratory samples should imitate the actual situation of large-scale production to the greatest extent, including cycle time, heating rate, addition of salt and alkali, and dyeing Post-processing, color matching, light source, etc.; therefore, mid-sample experiments must be done before large-scale production, and laboratory technicians must keep track and record them as reference materials for large-scale production; when large-scale samples are put into production, craftsmen must follow the relationship between small samples and large samples. Differences, past experience and mastery of dye properties, appropriate adjustments to the process, and the process for large sample production; the sample and the yarn used for production should be consistent, the pre-treatment process and post-treatment process should be consistent, and yarn replacement should be repeated The dye mother solution for making small samples should not be stored for too long to avoid changes in dye concentration and strength;
6. Operational factors
Operation by the person who made small samples It is necessary to standardize and use dyes scientifically, increase the training of operators, reduce the types of additives used, and use accurate measuring instruments;
7. Other factors
The water used for small samples should be consistent with that of large-scale production, and soft water should be used as much as possible. The pH value of soft water should be controlled at around 7.0 to ensure the stability of the dyeing pH value; strengthen the quality testing of auxiliaries; raw cotton and ingredients between different batches When using cotton, the laboratory must repeat the sample before dyeing. If the color light changes, it must be adjusted in time; pre-treatment is the basis of dyeing. If the pre-treatment is not good, the foundation is not solid, and dyeing will also have poor reproducibility. Pay attention to the yarn. pre-processing. </p






