Functional fabric-flame retardant fabric
With the development of the economy and the improvement of the national legal system, the promotion and application of flame-retardant textiles has attracted the attention of the whole society. There is a lot of development and research on flame-retardant fabrics abroad. Some industrially developed countries formulated flame-retardant regulations for textiles as early as the mid-1970s. In recent years, the requirements have become higher and higher, and the regulations have become more and more detailed. The Fire Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China, which came into effect on September 1, 1998, has promoted the development of flame-retardant textile technology in my country. In recent years, my country’s research and development on flame-retardant textiles has gradually increased and considerable progress has been made. With the acceleration of urban modernization, the development of tourism and transportation industries, and the increase in demand for export textiles, there is a huge potential market for flame-retardant textiles. According to the survey, the consumption of flame retardant products is mainly distributed in the steel casting industry, fire service industry, chemical manufacturing industry, etc. Public service units mainly include: hospitals, military, and forest fire-fighting service teams. In addition to clothing, flame-retardant textiles for cars, trains, and airplanes, as well as seat covers, curtains, and decorative fabrics for hotels, theaters, auditoriums, and other places also have endless potential.
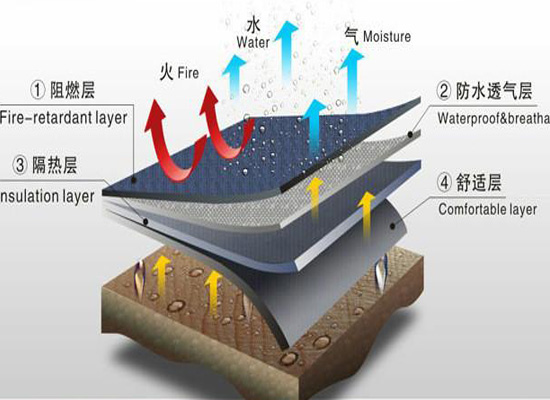
Two main ways to achieve flame retardant functionality in textiles~
1. Apply the flame retardant layer on the surface of the fabric or penetrate into the fabric using post-finishing methods.
Currently, the internationally popular flame retardant technologies include Proban and CP flame retardant.
Proban is a water-soluble flame retardant that easily penetrates into the fiber, making it flame retardant. It is a finishing flame retardant for cotton fiber and its blended fabrics. Its main feature is that after using this flame retardant to produce and finish, permanent cross-linking is formed inside the fabric, thus making it flame retardant. performance and maintain the original performance of the fabric.
CP flame retardant fabric is a flame retardant fabric produced using imported technology and imported environmentally friendly flame retardants. It is superior to polybenzene flame retardant fabric. The most important thing is that the formaldehyde content achieved after washing and formaldehyde capture treatment can fully meet foreign standards. And the formaldehyde content will not rebound over time. However, the fabric strength loss caused by CP flame-retardant processing is slightly greater than that of proben flame-retardant fabrics, and the price is higher.
2. The flame retardant with flame retardant function is added to the fiber through polymer polymerization, blending, copolymerization, composite spinning, joint extrusion modification and other technologies to make the fiber flame retardant, that is, flame retardant fiber.
The flame-retardant fibers currently used in domestic and foreign markets mainly include: aramid, flame-retardant acrylic, flame-retardant viscose, flame-retardant polyester, flame-retardant vinylon, etc. In addition to excellent flame retardant properties, the flame retardant fabrics produced using these fibers are most famous for their strong washability. Since they are flame retardant fibers themselves, ordinary industrial washing will not affect their flame retardancy. performance, it is called a permanent flame retardant fabric.
Flame-retardant products produced using flame-retardant fibers have the following characteristics~
1. Excellent permanent flame retardant and fire retardant properties. Washing and friction will not affect the flame retardant properties.
2. Good safety. When the fiber encounters fire, it releases low smoke and does not release poisonous gas.
3. Using conventional fiber as the carrier, it does not produce harmful elements and meets environmental protection requirements.
4. Good thermal insulation, providing all-round thermal protection.
5. The fabric has the moisture absorption and release properties of conventional fibers, and has the characteristics of soft feel, comfort, breathability, and warmth.
6. Post-finishing flame retardant is mainly used for cotton or low-proportion chemical fiber fabrics, and flame-retardant fibers use various chemical fibers as carriers to give full play to the excellent properties of various chemical fibers.
Flame retardant fabrics have a wide range of applications and can be used to make protective clothing and special functional clothing. They are widely used in the military, firefighting, petroleum, electric power, natural gas, metallurgy, machinery, mining, chemical industry, aviation, shipping and other industries; to make general clothing, Especially children’s clothing, pajamas, etc.; making home and hotel decoration supplies, such as carpets, curtains, bedding, etc.; industrial machine covers, tents, etc.
Why do we need flame retardant treatment~
Fabrics are an indispensable and important part of people’s lives, but fabrics are generally easy to burn, leading to fires. According to statistics, at least about 50% of fires in the world are caused by burning fabrics. The easy-to-understand function of fabric flame retardants is a chemical additive that makes fabrics flame retardant or otherwise, thereby reducing the risk of fire.
Flame retardant mechanism of flame retardant fabric~
Under the action of an external heat source, when the temperature reaches 260°C, the polyester fabric begins to soften. When the temperature continues to increase to 280°C, the polyester undergoes thermal oxidative degradation, producing volatile flammable products, which burn under the action of an open flame, producing Active oxygen free radicals and hydrogen free radicals cause further degradation of polyester fabrics. Polyester uses the heat released during the combustion process as a heat source, making the fabric furtherDegradation occurs, allowing the combustion process to continue.
From the above analysis of the combustion mechanism of polyester, it can be seen that the combustion process of polyester is a cyclic process of interaction between heat source, fabric and oxygen. Flame retardant finishing refers to post-finishing the fabric to reduce its flammability when exposed to external heat sources, slow down the spread of combustion, and quickly extinguish the flame after the external heat source is removed. For the burning process of fabrics, flame retardancy is to cut off the circulation system of the interaction between the heat source, fabric and oxygen.
Theoretically, the flame retardant mechanism can be physical action, chemical action or a combination of both. Flame retardant mechanisms can be divided into the following categories:
Decomposition of endothermic flame retardant mechanism
The flame retardant undergoes endothermic decomposition reactions such as phase change, dehydration, etc. when heated. At this time, the flame retardant can absorb a certain amount of heat energy and reduce the heating of the fabric, thereby reducing the thermal decomposition of the fabric and the generation of flammable gases. . Endothermic flame retardancy is mainly reflected in inorganic flame retardants, such as magnesium hydroxide, aluminum hydroxide, etc. The decomposition process and decomposition products of inorganic flame retardants can absorb a large amount of heat energy.
Covering flame retardant mechanism
Flame-retardant covering is a chemical change that occurs when the flame retardant is heated and burns, and the flame-retardant substance solidifies on the fabric, forming an insulating covering layer on the surface of the fabric. The covering layer can play an insulating role, blocking the communication between the fabric and the heat source and oxygen, and can hinder the diffusion of flammable gases and block their interaction, thereby acting as a flame retardant. Both inorganic and organic flame retardants have a covering flame retardant mechanism. For example, ammonium polyphosphate flame retardants have a covering flame retardant mechanism.
Fiber modified flame retardant mechanism
Fabrics can obtain unique functions through fiber modification, reducing flammability or improving flame retardancy, such as:
1) It can improve the melting performance of the fabric, causing the fiber material to soften, shrink, and melt before thermal cracking, turning into molten droplets and dripping, and the heat is taken away to make the flame self-extinguishing;
2) By introducing aromatic rings or aromatic heterocycles into fiber macromolecules, the density and cohesion between fiber molecular chains are increased, thereby improving the heat resistance of the fiber;
3) By modifying the fiber, for example, cross-linking and cyclizing macromolecular chains, forming complexes with metal ions, etc., the molecular structure of the fiber is changed, thermal cracking is inhibited, and the generation of flammable gases is reduced.
Catalytic dehydration to carbon flame retardant mechanism
During the heating process, the flame retardant promotes the dehydration, cyclization and cross-linking processes of the fiber by changing the thermal cracking of the fiber, thereby forming a carbon layer. The formation of the carbon layer can reduce the generation of flammable gases and can also cover and insulate fabrics. Most of the flame retardants that work with this flame retardant mechanism are phosphorus-containing flame retardants. It is generally believed that phosphates and organic phosphate compounds have a flame retardant effect because they undergo an esterification reaction with the hydroxyl groups in the fiber macromolecules, preventing the formation of L-glucose, further dehydrating the cellulose, and generating unsaturated double bonds. It speeds up the cross-linking reaction between cellulose molecules, increases the carbon residue generation rate of the fabric, and achieves the purpose of flame retardancy.
Vapor phase flame retardant mechanism
There are two main theories for the gas phase flame retardant mechanism, one is the gas dilution theory, and the other is the free radical theory. The gas dilution theory believes that the mechanism of flame retardancy is due to the thermal decomposition of flame retardants to produce non-combustible gases. These gases dilute the concentration of flammable gases, resulting in insufficient oxygen during the burning process of the fabric, and the diffusion of such gases causes It can dissipate heat and cool down, thus achieving the flame retardant effect; the free radical theory believes that the thermal cracking products of flame retardants can interrupt the combustion chain reaction, because the cracking products can capture a large amount of high-energy oxygen free radicals and hydrogen free radicals during the combustion process. base, thereby exerting a flame retardant effect. The main ones that work on the gas phase flame retardant mechanism are ammonium-containing flame retardants and halogen flame retardants. The former is a gas dilution mechanism, and the latter is a free radical theory.







